REPMUS – Robotic Experimentation and Prototyping with Maritime Unmanned Systems, the largest operational experimentation exercise of unmanned systems in the world, took place in Portugal yet again, between September 9 and 27 (Troia and Sesimbra).
Over two weeks, INESC TEC mobilised more than 15 people from two research areas – robotics and autonomous systems and photonics – to participate in the world’s largest robotics exercise. Although the presence of INESC TEC robotics researchers is already quite common, the participation of photonics researchers was a novelty. And the “veterans” were able to break more records!
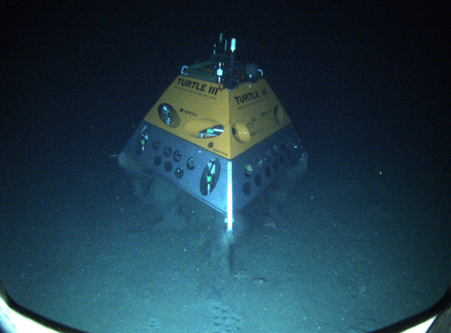
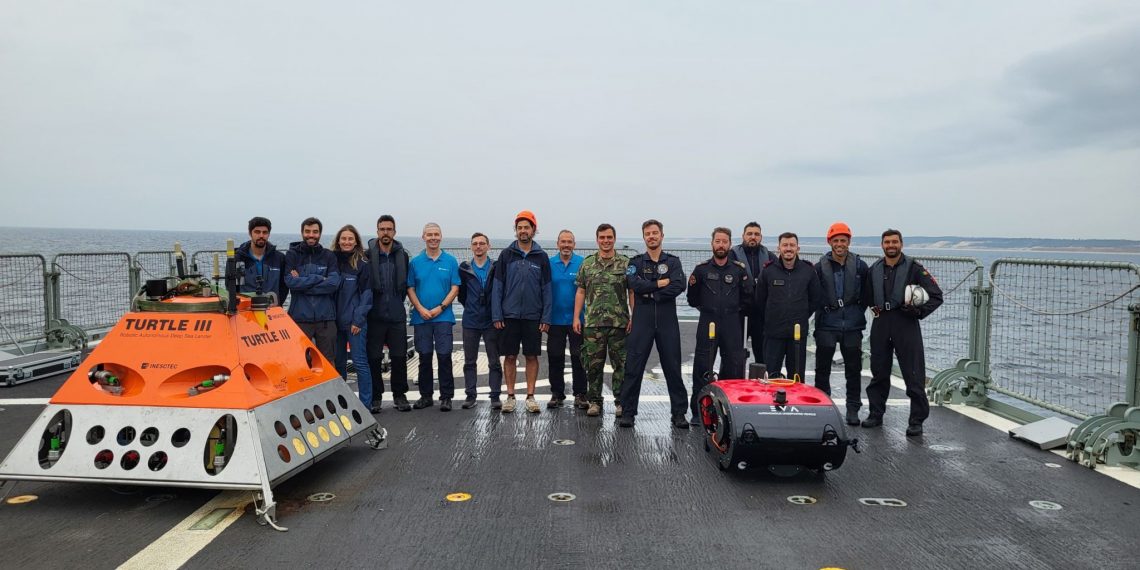
The autonomous robots EVA and Turtle III managed to operate at a depth of 830 meters, being the only ones in Portugal capable of doing so. In addition, INESC TEC was the only institution – among the 100 entities involved – to present a solution capable of simulating a threat to underwater cables, thanks to the Turtle underwater robot.
This was the first time autonomous and unmanned robots were tested for the in-depth protection of critical infrastructures. The EVA and TURTLE robots are the first robots – fully developed in Portugal – with demonstrated operational capacity for deep-sea operation, with unique features worldwide, since TURTLE is the only robotic lander vehicle with the possibility of remaining on the seabed, and capable of autonomous relocation.
During the exercise, several technologies and drones operating in different maritime environments were tested, i.e., surface, subsurface, air and land areas. REPMUS – organised by the Portuguese Navy – welcomed people from 23 countries and 20 ships, with close to 2000 participants.
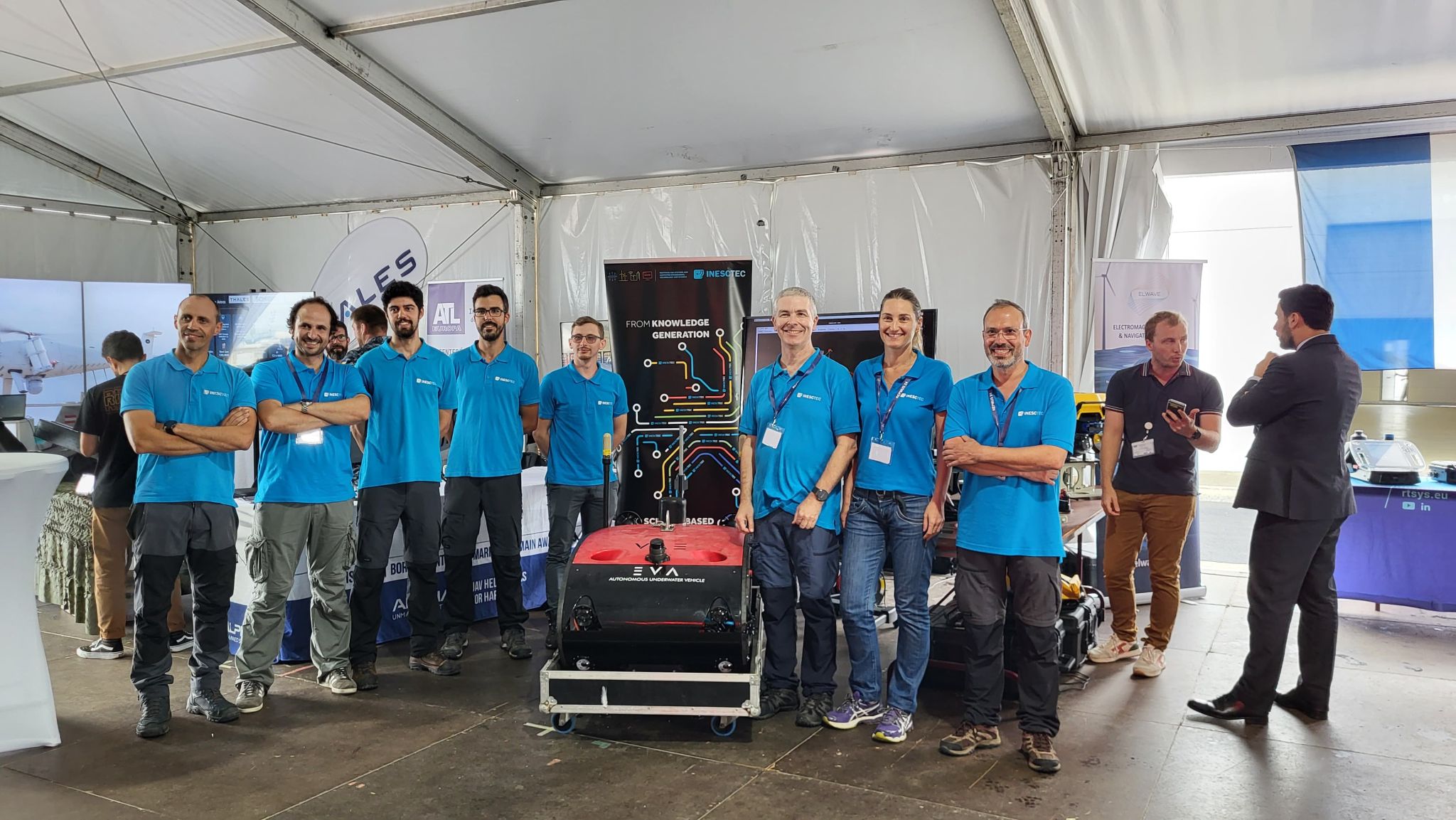

The participation of INESC TEC robotics and autonomous systems researchers
INESC TEC robotics and autonomous systems researchers participated in a real test of operational capacity to protect critical infrastructures at great depth. In this two-stage mission, a first called RED force – which aimed to evaluate the ability to intervene and simulate attacks to critical infrastructures, e.g., underwater cables – and a second called BLUE force – which aimed to evaluate the ability to detect and protect threats -, INESC TEC participated with the EVA and TURTLE submarine robots.
In the first phase, the RED force, after laying a submarine cable more than 800m deep, researchers used the EVA robot to perform the reconnaissance of the settlement site and define a precise location. Then, the robotic lander TURTLE was dropped and programmed to be placed on the seabed next to the target submarine cable, in order to signal threats.
During the BLUE force, EVA was used to identify and obtain the precise geolocation of the threat made by TURTLE. The mission was carried out successfully. The TURTLE returned to the surface and was collected after spending five days on the seabed – more than 800 meters. The second stage featured the participation of several resources used by NATO navies. Only the INESC TEC robots – with fully Portuguese technology – and a Norwegian robot were able to geolocate the threat.
“The operations performed in collaboration with the Portuguese Navy were carried out from different vessels, namely the NRP D. Carlos I and the NRP Sines, demonstrating the operational capacity and the Portuguese Navy ability to – together with partners – operate innovative means and state-of-the-art technology for crucial missions, focusing on the deep sea”, explained José Miguel Almeida, researcher at INESC TEC.
Also, within the scope of these naval exercises, the INESC TEC team resorted to the autonomous underwater vehicle EVA to simulate submarines’ rescue in emergency situations. In this case, the Navy submarine NRP Harpoon landed on the seabed simulating an emergency.
The first exercise addressed the use of autonomous underwater vehicles for the geolocation and survey of the submarine’s state. In the second exercise, the autonomous underwater vehicle was used to support and guide a team of Navy divers to access the NRP Arpão and provide assistance, carrying equipment on board and removing other elements. The EVA robot was used to locate the position of the submarine accurately, indicating the exact location to the divers, besides being able to make visual and sonar recognition of the submarine conditions.
“It was also possible to address a request from the Dutch Navy and the TNO R&D institute to search for and collect acoustic monitoring equipment lost on the seabed. In this case, our team was able to locate and collect the equipment through the EVA robot, with an operation conducted from INESC TEC’s Mar Profundo vessel,” said José Miguel Almeida.
During the Distinguished Visitors Day, the INESC TEC stand showcased the underwater robotic systems EVA and Trutle III, and the autonomous surface vehicle PORTUS, as well as several results obtained during the exercises. The INESC TEC stand welcomed renowned personalities like Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa, President of the Republic, and Nuno Melo, the Minister of National Defense.

The presence of photonics researchers
Among the 100 participating entities, INESC TEC also stood out for the installation of the DAS (Distributed Acoustic Sensing) system on the Sagres underwater cable, located at Altice’s facilities in Sesimbra. “This equipment made it possible to monitor the movement of ships and other events in the Troia area during the exercise”, explained Orlando Frazão, researcher at INESC TEC.
The data collected will be analysed by the Portuguese Navy in collaboration with INESC TEC, through signal processing. In the future, both institutions will discuss new endeavours, aiming at the use of DAS technology in underwater cables throughout the Portuguese territory. As a result of this collaboration, a project has already been submitted to FCT, within the scope of PRR – “RE-C05-i08 – Ciência Mais Digital”. “This project aims to develop an advanced solution for the detection of events in underwater cables, through the data obtained with DAS technology, using machine learning and AI techniques,” explained Orlando Frazão. The application features the Portuguese Navy and INESC TEC competences in Artificial Intelligence and Decision Support and Applied Photonics.
The researchers mentioned in this news piece are associated with INESC TEC, IPP-ISEP and UP-FCUP.


 News, current topics, curiosities and so much more about INESC TEC and its community!
News, current topics, curiosities and so much more about INESC TEC and its community!